基本阴影贴图
基本的阴影贴图算法分为两步。首先,从灯光的角度渲染场景。仅计算每个片段的深度。接下来,场景将照常渲染,但需要进行额外的测试以查看当前片段是否在阴影中。
“在阴影中”测试实际上很简单。如果当前样本在同一点上比阴影贴图离灯光更远,这意味着场景包含一个离灯光更近的对象。换句话说,当前片段处于阴影中。
下图可能有助于您理解原理:
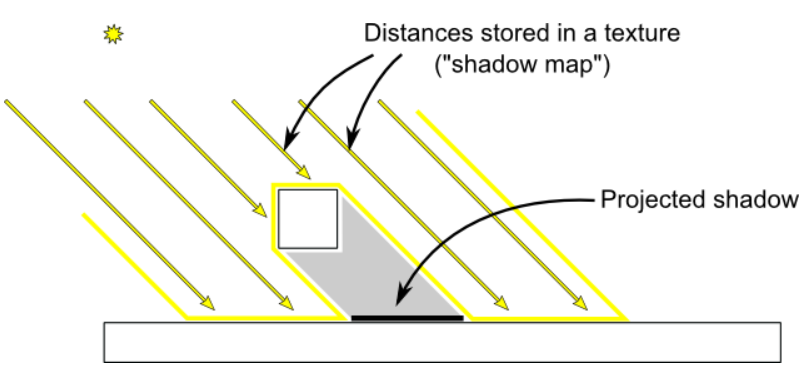
渲染阴影贴图
在本教程中,我们将只考虑平行光——距离如此之远,以至于所有光线都可以被视为平行的光。因此,渲染阴影贴图是使用正交投影矩阵完成的。正交矩阵就像通常的透视投影矩阵一样,只是不考虑透视——无论物体在相机附近还是远处,它看起来都是一样的。
设置渲染目标和MVP矩阵
在这里,我们使用1024x1024 16位深度纹理来包含阴影贴图。对于阴影贴图,16位通常就足够了。请随意尝试这些值。请注意,我们使用的是深度纹理,而不是深度渲染缓冲区,因为我们稍后需要对其进行采样。
// The framebuffer, which regroups 0, 1, or more textures, and 0 or 1 depth buffer.
GLuint FramebufferName = 0;
glGenFramebuffers(1, &FramebufferName);
glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, FramebufferName);
// Depth texture. Slower than a depth buffer, but you can sample it later in your shader
GLuint depthTexture;
glGenTextures(1, &depthTexture);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, depthTexture);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0,GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT16, 1024, 1024, 0,GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT, GL_FLOAT, 0);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
glFramebufferTexture(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GL_DEPTH_ATTACHMENT, depthTexture, 0);
glDrawBuffer(GL_NONE); // No color buffer is drawn to.
// Always check that our framebuffer is ok
if(glCheckFramebufferStatus(GL_FRAMEBUFFER) != GL_FRAMEBUFFER_COMPLETE)
return false;用于从灯光的视角渲染场景的MVP矩阵计算如下:
glm::vec3 lightInvDir = glm::vec3(0.5f,2,2);
// Compute the MVP matrix from the light's point of view
glm::mat4 depthProjectionMatrix = glm::ortho<float>(-10,10,-10,10,-10,20);
glm::mat4 depthViewMatrix = glm::lookAt(lightInvDir, glm::vec3(0,0,0), glm::vec3(0,1,0));
glm::mat4 depthModelMatrix = glm::mat4(1.0);
glm::mat4 depthMVP = depthProjectionMatrix * depthViewMatrix * depthModelMatrix;
// Send our transformation to the currently bound shader,
// in the "MVP" uniform
glUniformMatrix4fv(depthMatrixID, 1, GL_FALSE, &depthMVP[0][0])着色器
此过程中使用的着色器非常简单。顶点着色器是一个传递着色器,它简单地计算顶点在齐次坐标系中的位置:
#version 330 core
// Input vertex data, different for all executions of this shader.
layout(location = 0) in vec3 vertexPosition_modelspace;
// Values that stay constant for the whole mesh.
uniform mat4 depthMVP;
void main(){
gl_Position = depthMVP * vec4(vertexPosition_modelspace,1);
}片段着色器同样简单:它只是在位置0(即在我们的深度纹理中)写入片段的深度。
#version 330 core
// Ouput data
layout(location = 0) out float fragmentdepth;
void main(){
// Not really needed, OpenGL does it anyway
fragmentdepth = gl_FragCoord.z;
}渲染阴影贴图的速度通常是普通渲染的两倍多,因为只写入低精度深度,而不是深度和颜色;内存带宽通常是GPU上最大的性能问题。
结果
生成的纹理看起来像这样:
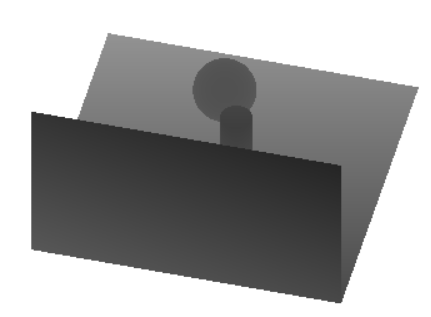
原文:https://www.opengl-tutorial.org/intermediate-tutorials/tutorial-16-shadow-mapping/#basic-shadowmap